
| |
Background on War & Peace
|
The War & Peace category encompasses situations around the world
where the US is involved in a prolonged military intervention,
or where the US is involved in prolonged peace negotiations:
- Syria: Overthrow of the Assad regime
- Ukraine: Russian invasion of Ukraine
- Gaza: Hamas invasion of Israel
- Houthis (vs. Israel) and Yemen (vs. Saudi Arabia)
- Former Soviet Union: Chechnya, Armenia and Azerbaijan
- ISIS & Terrorism: US troops in the Mideast, and assassinations
- UAE-Israeli Treaty: Peace treaties with United Arab Emirates and Bahrain
- Islam: Background on Shi'ite vs. Sunni Islam and its relevance for the Middle East.
- Syria: the US intervention in the Syrian Civil War.
- Israel & Palestine: history since 1948 through the current peace process.
- Persian Gulf: situation regarding Kuwait, Iraq, Iran, and the Gulf War.
- Iran: The U.S. and U.N. finalized a "nuclear deal" with Iran in 2015.
- Central Asia: the War on Terrorism, focusing on Afghanistan.
- Al Qaeda: The origins of our enemy in the War on Terror.
Other foreign affairs are covered in other pages of this web site:
- The Balkans: history of Kosovo, Bosnia, and other former Yugoslav republics.
- Foreign Policy: Other world hotspots, as well as strategy and principles of foreign affairs.
- China: Specifics regarding China & Taiwan, including human rights & trade issues.
- Defense: Defense spending, weapons planning, and other military issues.
Overthrow of the Assad regime in Syria
- Bashar al-Assad:
The President of Syria fled the country on Dec. 8, 2024, when rebels took the capital, Damascus. Assad was in power since 2000, when his father died; Hafez al-Assad had ruled Syria since 1971 (the mainstream media calls this "Assads' 50-year reign").
- Syrian Civil War:
The Assad regime almost fell in 2014, after three years of civil war. Russia and Iran came to Assad's aid, and have been aiding the Syrian regime ever since. But Russia was busy with the Ukraine war and could not aid Assad in 2024.
- Iran and Hezbollah: Iran aided Assad through "proxies", primarily Hezbollah in Lebanon, but Hezbollah was weakened by their involvement in the Israel-Gaza war. The Syrian rebels took advantage of the lack of support from Russia and Iran, and Assad's army collapsed in less than two weeks.
- Hay'at Tahrir al-Sham (HTS):
The lead rebel group is called HTS, which means "Organization for the Liberation of the Levant." HTS was originally an offshoot of Al Qaeda, and were then called the "al-Nusrah Front." They broke ties with Al Qaeda in 2016 but are still on the U.S. list of terrorist organizations.
- Abu Muhammad al-Jawlani:
The leader of HTS uses a nom de guerre which roughly means "Father of the Prophet; the Man from Golan." Golan is the region of Syria occupied by Israel since 1967 and annexed in 1981. Some transliterations use "Golani", and indeed his family came from the Golan region.
- Kurdish and Turkish rebel groups:
HTS initiated the 2024 rebellion, but were joined by several other rebel groups. The largest are the Kurds in the east (on the Syria-Iraq border) and Turkish-supported rebels in the north (on the Syria-Turkey border). The Kurds and Turks both held substantial territory before the 2024 uprising. The three main rebel groups have differing goals, but it's yet to be seen how they get along in post-Assad Syria.
- Al-Tanf United States military base::
U.S. troops have been in Syria since 2016; we invaded Syria as part of the Iraq-ISIS-caliphate war at that time. We have about 900 U.S. troops on the ground in Syria (and 2,500 more across the border in Iraq). The U.S. has bombed ISIS sites in Syria to prevent a "resurgence of the Islamic State in eastern Syria" and in response to ISIS attacks in support of the Gaza war, since 2023 and currently continuing. There's another rebel group, the Free Syrian Army, around the U.S. base, which is on the Iraq-Syria-Jordan border. U.S. troops did not participate in the 2024 rebellion (except bombing ISIS) and President-elect Trump has indicated he wants to keep it that way.
- Does ISIS play a role? No, ISIS has not joined in the rebellion, which could be in part because of the ongoing U.S. attacks against ISIS sites in Syria. The U.S. and allies succeeded in mostly pushing ISIS out of Iraq and Syria in 2016-2019, but the terrorist group still actively exists in North Africa (ISIS-Libya) and in Afghanistan. A more accurate name for the group is "ISIL", substituting "Levant" for "Syria." The Levant includes Gaza, Israel, Lebanon, and Syria -- which is a more accurate description of ISIS' territorial ambitions. It's unclear in 2024 what ISIS will do in post-Assad Syria.
- Shia vs. Sunni: The Syrian Civil War focuses heavily on religion within Islam. Assad was Shi'ite, and was supported by Shi'ite Iran and Shi'ite Iraq (mostly). Syria is majority Sunni, which means they were ruled for 50 years by a religious minority. Hezbollah is Shi'ite; HTS and ISIS are Sunni; those are basically the two sides in the Syrian Civil War.
- Iran vs. Saudi Arabia: Iran is the largest Shi'ite country; Saudi Arabia is the largest Sunni country; those two are the leaders of their respective halves of the Muslim world. Beyond the Syria conflict, the bigger picture focuses on Iran vs. Saudi Arabia -- Russia and its allies back Iran and the Shi'ites; the United States and its allies back Saudi Arabia and the Sunnis.
JD VANCE: Trump said "no" when a lot of them wanted a ridiculous war including Syria (Oct 2024)
Kamala HARRIS: US-Iraq partnership role after Defeat ISIS coalition (Feb 2024)
Donald TRUMP: I beat ISIS in literally three months; knocked them out (Jan 2024)
Nikki HALEY: Go hard after Iranian infrastructure in Syria & Iraq (Dec 2023)
Donald TRUMP: Abraham Accords end the centrality of Arab-Israeli conflict (Apr 2023)
Donald TRUMP: Withdrew from Syria, but left soldiers to keep the oil (Feb 2020)
Tulsi GABBARD: Indefinite stay in Syria IS "endless war" (Oct 2019)
Tulsi GABBARD: End the regime change war in Syria (Oct 2019)
Bernie SANDERS: End Syrian conflict; pull out U.S. troops (Feb 2019)
Nikki HALEY: Military action & sanctions against Syrian chemical weapons (Apr 2018)
Mike HUCKABEE: Eradicate ISIS like you would eradicate any cancer (Jan 2016)
Bernie SANDERS: Work with Russia & Iran to get rid of Assad in Syria (Jan 2016)
Chris CHRISTIE: There'll be no peace in Syria while Assad is in charge (Jan 2016)
Marco RUBIO: Boots on ground in Syria; coordinate with Kurds (Nov 2015)
Mike HUCKABEE: We are at war with radical Islam (Nov 2015)
Kristi NOEM: Aid the Syrian opposition with training & equipment (Sep 2014)
Marco RUBIO: Equip and train non-jihadist Syrians to topple Assad (Aug 2013)
Joe BIDEN: Syria's Assad must go, but carefully vet who gets aid (Mar 2013)
Joe BIDEN: Iran is isolated, and will be more so when Syria falls (Dec 2011)
War & Peace topics in the 2024 election cycle:
Russian invasion of Ukraine
- 2022 Invasion: In February 2022, Russia invaded Ukraine in the Donetsk and Luhansk region (known collectively as "Donbas" along Ukraine's southeastern border with Russia)
- Kyiv: Russian forces also invaded through Belarus, in an attempt to quickly reach Kyiv, Ukraine's capital, and topple the government.
- Donbas: Ukraine's army resisted and beat back the Russian army around Kiev, and the war devolved to a long conflict in Russian-occupied Donbas, with active fighting into 2024.
- Land Bridge: Russia succeeded in creating a "land bridge" to Crimea: a supply route to the southern region occupied since 2014.
- Annexation: Russia held a referendum vote in 2022 to annex 4 regions of the Ukraine (Donbas plus Kherson and Zaporizhzhia); "annexation" means the regions become part of Russia, as had been done in 2014 in Crimea. NATO and most of the world do not recognize the results of the annexations.
- NATO: NATO countries, including the United States, have supplied armaments and funds (but not troops) to build up the Ukrainian armed forces. Russia has objected, but the arms supply is open (not secretive like was done against Russia in Afghanistan)
- Counterattack: In mid-2024, Ukraine managed to occupy some land on the Russian side of the border, using US- and NATO-provided weapons.
Biden announced in November 2024 that Ukraine was allowed to fire US-provided missiles into Russia, which was previously disallowed.
- Unprovoked? The mainstream media routinely use the phrase "Russia's unprovoked invasion of Ukraine" (Link), but the Russian government felt provoked for many years by potential NATO membership for Ukraine, which would imply an American troop presence and missile presence adjacent to Russia's heartland (Link).
J.D. VANCE: I'm not pro-Russia; I'm anti-nuclear-war (Nov. 2024)
Donald TRUMP: End Ukraine war by negotiating, not by one side winning (Sep 2024)
Kamala HARRIS: Brought 50 NATO countries into righteous defense of Ukraine (Sep 2024)
Joe BIDEN: Putin is a war criminal and won't stop at Ukraine (Jun 2024)
Tim_SCOTT: Our vital interest in Ukraine is degrading Russian military (Nov 2023)
Vivek RAMASWAMY: Defend our border, not Ukraine's (Aug 2023)
Ron DeSANTIS: Europe should pull their weight and fund Ukraine war (Aug 2023)
Robert F. KENNEDY Jr: Russia's invasion of Ukraine is brutal; but not "unprovoked" (Jun 2023)
Nikki HALEY: War in Ukraine is about freedom--one we have to win (Jun 2023)
Chris CHRISTIE: Trump not backing Ukraine makes him Putin's puppet (Jun 2023)
Tim WALZ: Support Ukraine; withdraw investments from Russia & Belarus (Apr 2022)
Joe BIDEN: Military & humanitarian assistance, but no troops to Ukraine (Mar 2022)
Gaza / Hamas / Lebanon / Hezbollah
- October 7: On Oct. 7th, 2023, Hamas invaded southern Israel, killing over 1,200 civilians and kidnapping over 200 more hostages. About 100 civilians are still being held hostage as of the 2024 election. Israel has fought a war against Hamas since then, with the stated purpose of rescuing the hostages and destroying Hamas.
- Fatah: Hamas is the ruling party in the Gaza strip, the part of Palestine on the Mediterranean Sea. They fought a civil war in 2007 against Fatah, who are the ruling party of the West Bank, the part of Palestine on the Jordan River. Fatah has largely stayed out of the Hamas war, and could theoretically take over
- Hamas: Hamas was elected in 2006 in Gaza, but have not held elections since. They are considered a terrorist group by most countries, including the U.S. They do not recognize the right of Israel to exist (Fatah does).
- From the River to the Sea: Hamas' slogan means their goal is to control all the land between the Jordan River to the Mediterranean Sea, which implies the elimination of Israel. That's the opposite of...
- Two-state solution: The two states, Israel and Palestine, would split that territory as two sovereign countries, as was the United Nations plan in 1948, and is still the United States policy preference today. Some Israeli extremists call for a one-state solution, which would be all Israel from the river to the sea.
- War crimes? The International Criminal Court charged both Israeli leaders and Hamas leaders with war crimes. Only extremist candidates like Jill Stein support that action; the Democratic and Republican stances are identical in strong support of Israel and continuing supplying Israel with funding and weapons.
HARRIS: Israeli long-term security needs negotiated 2-state solution (Jun 2024)
BIDEN: 3-stage plan for Gaza; only Hamas opposes it (Jun 2024)
TRUMP: Unbreakable alliance with the state of Israel (Feb 2017)
JILL STEIN (Green Party nominee): Charges Israel, US leaders with war crimes (Nov 2023)
- Iran involvement: Israel assassinated some Hamas officials in Iran, and Iran and Israel followed up with hundreds of missiles and drones. But Iran has mostly been fighting Israel through "proxies", which include Hamas in Gaza and two other terrorist groups...
- Hezbollah in Lebanon: Hezbollah began firing missiles into Israel on Oct. 8, 2023, in support of Hamas. The missiles were mostly shot down by Israel's defensive "Iron Dome," but Israel invaded Lebanon in autumn 2024 to end the missile barrages.
- Houthis in Yemen: Shortly after the Oct. 7 attack, Houthi rebels began firing at commercial shipping in the Red Sea. That's the outlet from the Suez Canal, and some commercial ships rerouted around Africa instead of risking Houthi missiles to use th Suez Canal. The United States and other countries defended commercial shipping (i.e. U.S. warships fired on the Houthis, the most important direct American military involvement in the Gaza War).
- Saudi Arabia: Many analysts claim that the timing of the Gaza attack was intended to prevent Saudi Arabia from signing the next round of the Abraham Accords. In that theory, Iran got Hamas to attack Israel to prevent a peace treaty between Israel and Saudi Arabia (Iran's arch-enemy), which seemed about to happen in late 2023. However, Hamas' timing was actually long-planned in advance to mark the 50th anniversary of the Yom Kippur War of October 1973. But Iran is nonetheless an important focus of the Gaza War...
TRUMP: Hamas attacked Israel when Iran got rich; I kept Iran broke (Sep 2024)
VANCE: Trump deterred Iran; Biden-Harris unfroze $100B (Oct 2024)
BIDEN: Contain Iran; degrade the Houthis; include Saudi Arabia (Mar 2024)
WALZ: Build coalition against Iranian nuclear weapons (Oct 2024)
War & Peace topics in the 2020 election cycle:
Former Soviet Union
- Armenia and Azerbaijan: Today's war between Armenia and Azerbaijan over the disputed territory of Nagorno-Karabakh already reverberates beyond the Caucasus. It shows exactly what happens when Washington abdicates its diplomatic authority and capability, as it has done in the Caucasus. Our unwillingness to bring about a genuine mediation has helped precipitate this war. (The Hill; more on Nagorno-Karabakh in our Foreign Policy backgrounder)
- Chechnya: Chechnya has made progress in suppressing insurgency, reconstructing cities and improving its image and official economic indicators. Its peace is fragile, a result not only of highly personalized governance reliant on repression and arbitrariness that Moscow tolerates and covers up, but also economic inequality, poor social infrastructure, lack of genuine reconciliation and almost full impunity for abuses. (ICG)
- PRO-Ukrainian Crimea: Russia's occupation of Crimea and its increasing militarization of the peninsula is a threat to our common security. Russian occupation authorities continue their assault on human rights and fundamental freedoms, brutally silencing critics in civil society and the media, and curtailing religious freedom. (State Dept.)
- ANTI-Ukrainian Crimea:
Moscow expressed concern about the fate of ethnic Russians in Crimea, but no evidence showed any threat to them. The Kremlin applies the principle of self-determination selectively; Moscow responded to the desire of Chechens for independence from Russia after the Soviet collapse with two bloody conflicts. (Brookings 2020)
- TRUMP: Refuses to consider mass killings of Armenians as genocide (Dec 2019)
- BIDEN: Acknowledge the Armenian Genocide of the early 1900s (Mar 2007)
- TRUMP: Russia violates the Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces treaty (Feb 2019)
- BIDEN: Inviolate borders for Ukraine; no spheres of influence (Nov 2017)
- PENCE: Russian "reset" is appeasement and invites aggression (Apr 2014)
- HARRIS: Trump embracing Korean & Russian dictators is a threat (Jun 2019)
- NEWS: Latest statements on Russia / Ukraine from presidential candidates and political pundits
ISIS & Terrorism
- U.S. lives lost in GWOT: 7,000 U.S. troops have been killed in war from 2001 through the end of 2018: 2,298 in Afghanistan and 4,572 U.S. troops in Iraq. (FCNL)
- U.S. troops in Syria: The reinforcements [in Syria to counter the Russians], which add about 100 troops to the more than 500 U.S. forces already there, represent a show of force. (N.Y.Times, 2020). French and British special forces were fighting side by side with Americans and Kurds. A recent estimate says about 4,000 "foreign fighters" in Syria and Iraq come from EU countries. (Brookings 2019) [U.S. troops remain in Syria a year after President Trump's promise to remove all U.S. troops--Ed.]
- U.S. troops in Iraq: The United States plans to reduce its military force in Iraq from the current 5,200 to about 3,500 by November [2020]. (Military Times)
- U.S. troops in Afghanistan: In January 2015, NATO launched the Resolute Support Mission (RSM) to train, advise and assist Afghan security forces and institutions. Currently (Oct. 2020), it numbers around 12,000 troops from 38 NATO Allies and partner countries. (NATO)
- Exiting Afghanistan:
Trump has announced that he wants to bring all US troops home from Afghanistan by Christmas.
Multiple officials told the Associated Press they had not been informed of any such deadline and military experts said it would be impossible to withdraw all 5,000 US troops in Afghanistan and dismantle the US military headquarters by the end of the year. (The Guardian)
- PRO-assassination:
There are two primary legal questions that have to be answered to decide if the president's act [assassinating Iraqi General Qasem Soleimani] was lawful in this situation. The first is whether the US could target Soleimani under international law, based on the United Nations charter. If so, the next question is whether the president can act without congressional authorization, consistent with constitutional law.
- ANTI-assassination: Article 51 of the UN charter prohibits the use of force against any person except only under the two circumstances: when the use of force was authorized by the UN Security Council and when a country acted in self-defense. It is clear that the UN Security Council did not authorize the strike [against Iraqi General Qasem Soleimani]. To meet the requirements for self-defense under international law, the US must have acted to avert an imminent attack.
- TRUMP: 2016: secret plan to defeat ISIS; 2018: caliphate gone (Jan 2018)
- BIDEN: Voted YES on authorizing use of military force against Iraq (Oct 2002)
- PENCE: Voted YES on declaring Iraq part of War on Terror with no exit date (Jun 2006)
- HARRIS: Bring the troops home from post-9-11 wars (Jul 2019)
- Libertarian Party nominee Jo JORGENSEN: Bombings in Middle East aren't a boost to Western security (May 2020)
- Socialist Party nominee Gloria LA RIVA: Exit Iraq immediately, and pay reparations (Jan 2008)
- TRUMP: We've beaten ISIS in Syria; bring US troops home (Dec 2018)
- NEWS: Latest statements on GWOT / War on Terror from presidential candidates and political pundits
Israeli-Arab Relations
- PRO-West Bank Settlements: Israel advanced plans for over 2,700 West Bank homes. The approvals brought the annual total of housing units advanced to 12,159, in what the Peace Now settlement watchdog said was a record-breaking figure that beat out last year's number by nearly 4,000.
- ANTI-West Bank Settlements: The Israeli government approved the construction of another 5,000 settlement units in the Occupied Palestinian Territory, including East Jerusalem, primarily in areas deep inside the West Bank.
- PRO-Jerusalem Embassy:: There has long been pressure from pro-Israel politicians in Washington to move the embassy to Jerusalem, and Trump made it a signature promise of his 2016 election campaign. Trump acted under a 1995 law that requires the United States to move its embassy to Jerusalem, but to which other presidents since then - Bill Clinton, George W. Bush and Barack Obama - consistently signed waivers. (Reuters)
- ANTI-Jerusalem Embassy: Both the Palestinians and the Israelis claim Jerusalem as their capital, and the city contains sites sacred to both Jews and Muslims. Israel has controlled West Jerusalem since 1949 [when Israel was founded]. Israel captured East Jerusalem in 1967 and annexed that half of the city. The international community considers East Jerusalem occupied territory. But that half of the city also contains sites holy to all three major monotheistic religions. (Vox.com)
- 2020 Israel Peace deals ("Abraham Accords"):
- United Arab Emirates:In August 2020, the UAE-Israeli peace deal became only the third Arab-Israeli peace deal (after Egypt in 1979 and Jordan in 1993). But it has opened the door to a panoply of additional Israeli peace deals....
- Bahrain normalized relations with Israel in September 2020. Bahrain borders the Persian Gulf, as does the UAE -- hence making peace with other Persian Gulf nations more likely (especially Qatar & Oman).
- Sudan seems likely to make a peace deal with Israel in early 2021, in exchange for U.S. removal of Sudan from the U.S. terrorist watch list. Sudan had a civil war and South Sudan split off in 2011; a revolution threw out the military dictator in 2019. Sudan had previously had active hostilities against Israel.
- Morocco seems likely to make a peace deal with Israel in early 2021, in exchange for U.S. recognition of the Moroccan occupation of Western Sahara. Sudan and Morocco deals would lead the way for normalization with Israel for other North African Muslim nations. (OTI)
- TRUMP: We're creating peace in Mideast; not the old-fashioned way (Sep 2020)
- BIDEN: Move the US Embassy to Jerusalem (Nov 1995)
- PENCE: Solidarity with Israel in its fight against terrorism (Apr 2002)
- HARRIS: Ok with Israeli settlements in Palestinian territory (Mar 2019)
- Birthday Party Nominee Kanye WEST: Praises Mideast peace treaties; expects Israel-Saudi next (Sep 2020)
- NEWS: Latest statements on Israel & Palestine from presidential candidates and political pundits
War & Peace topics in the 2016 election cycle:
Background on Islam

|
Understanding the religion of Middle Eastern countries helps in understanding many of the current "trouble spots" in the Middle East.
Muslims distinguish between two major branches of Islam, Shia Islam and Sunni Islam,
The map to the left (click on the map to enlarge it) indicates countries with:
- A Shi'ite majority (darker greens; Iran and Iraq)
- A large Shi'ite minority (medium greens; Lebanon and Yemen)
- A small Shi'ite minority (light greens; Turkey, Syria, Af-Pak)
- Sunni majority and Sunni rulers (tan; led by Saudi Arabia)
|
Several current Mideast trouble spots can be identified by whether the religion of the ruling group matches the religion of the majority of the population.
When the majority is Sunni and the Shias are in power, or vice versa, the country is often a "trouble spot."
That same analysis holds for determining which terrorist groups are on which side. Some details by country and group:
- In Iraq, Saddam Hussein was a Sunni, but Iraq is majority Shi'ite.
Hence Saddam's government, which was almost all Sunni, was seen by his Shi'ite population as a ruling elite.
When you read in the news about "Saddam loyalists fighting the government," it usually means "Sunnis who were once in power under Saddam, fighting against Shias now in power."
- Iran has a strong Shi'ite majority, and its rulers (the Ayatollahs) are also Shi'ite;
hence Iran is not likely to suffer from internal revolution. However, Iraq and Iran share a long border, and fought a long war in the 1980s:
the Shias of Iran supported the Shias of Iraq against the ruling Sunnis of Iraq (Saddam).
Now, post-Saddam, the Iranians are not opposed to the Shia Iraqi government.
- Saudi Arabia is the leader of the Sunni Muslim world; Iran is the leader of the Shi'ite Muslim world. Many Mideast conflicts are "proxy wars" between those two powers, with Saudi Arabia assisting the Sunni side and Iran assisting the Shia side (see Yemen below)
MIDEAST CONFLICTS BASED ON SHIA-SUNNI SPLIT:
- ISIS: ISIS is an anti-Shia group (i.e. Sunnis who oppose Shi'ite rule). The United States left post-war Iraq with a Shia Prime Minister, Nouri al-Maliki. But Iraq has a large Sunni minority, who feel disempowered (since Saddam was Sunni).
ISIS ("Islamic State in Iraq and Syria") began taking territory from al-Maliki government control in early 2014.
The United States sent 300 "advisers" to help the Iraqi army fight ISIS, in June 2014, after ISIS had captured substantial territory.
ISIS is more accurately known as ISIL, "Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant"; the Levant is the Eastern Mediterranean area that includes Syria, Lebanon, Israel, and Palestine.
ISIL had been fighting in Syria (against Assad's Shi'ite army) alongside Al-Qaeda, but broke ties with Al-Qaeda in Iraq.
ISIL's goal is to establish a "Caliphate," an Islamic State (hence their name), to replace the current governments.
ISIL's view of Islam often focuses on the Apocalypse (which is the same as in the Christian Bible): only when the Caliphate includes Jerusalem will the end times come.
- Kurdistan: The Kurds are an ethnic group in the Mideast, with an army known as the Peshmerga.
In the 2016 U.S. elections, an important issue is whether to increase support of the Kurds and/or the Peshmerga.
Western countries support the Peshmerga because of joint interest in defeating ISIS and Al Qaeda; but most western countries do not support an independent Kurdistan.
When politicians talk about supporting local groups without committing U.S. ground troops, they generally mean "give the Kurds money, arms, and U.S. air support."
For comparison. ISIS currently holds substantial territory in both Syria and Iraq, with a goal of establishing a religious Caliphate in their territory.
The Kurds, majority Sunni but a Shia minority, also hold substantial territory in both Syria and Iraq, and also look towards establishing a country, which they call Kurdistan.
- Al Qaeda: Al Qaeda is a Sunni group which is fighting against the Shi'ite governments in Syria, Iraq, and elsewhere.
In Syria, al Qaeda (and ISIS) oppose President Assad, whom the U.S. considers a terrorist dictator; i.e. they are on "our" side in Syria.
In Iraq, al Qaeda (and ISIS) oppose the Iraqi government, which the U.S. set up after Saddam; i.e., they are against "our" side in Iraq.
Al Qaeda is currently financed by Saudi Arabia, the country where Osama bin Laden came from.
But their original funding came from the United States because we supported al Qaeda's fight against the Soviet Union in Afghanistan in the 1980s.
Al Qaeda's goal is to remove all Western (non-Muslim) powers from the Muslim Holy Lands, which means Mecca and Medina in Saudi Arabia, plus Jerusalem in Israel.
- Syria has a Shi'ite minority (in other words, a Sunni majority) but is ruled by the Assad family, who are Shi'ite.
(The Assads call themselves "Alawite"; that is a Shi'ite sect).
The groups fighting in the Syrian civil war can be entirely divided along Shia-Sunni lines:
Assad is supported by Iran (a Shi'ite country), and by Hezbollah (a Shi'ite terrorist group);
the Syrian rebels are supported by the Saudi Arabia and the Emirates (Sunni countries), and by Al-Qaeda, a Sunni terrorist group.
- Red Line:
President Obama declared in August 2012 that Syria’s use of chemical weapons would cross “a red line for us,” necessitating U.S. military intervention.
Chemical weapon use was well established by August 2012.
That list of groups above is confusing, and President Obama had trouble figuring out in August 2012 which groups to help and which to attack. Or more specifically, how to explain to Americans that we should help some groups and attack others. Obama did try to enforce the “red line,” by planning aid to some groups and attacks on others, but the American public soundly rejected any support for Obama’s policy, and the policy was abandoned.
- Lebanon, until the 1980s, had a power-sharing arrangement among its different religious groups.
Then Syria intervened, because Assad (Shi'ite) wanted to "help" the large Shi'ite group in Lebanon.
Hezbollah, the Shi'ite terrorist group, has (in effect) ruled Lebanon, with Iran's and Syria's assistance, since that time.
- Bahrain has a Shia majority and Sunni rulers. The Arab Spring revolt in Bahrain in 2011 was put down by Saudi (Sunni) rulers.
- Yemen is split about 50-50 Sunni-Shia, but with Sunnis in control of the government.
The "Shia insurgency" is what they call their civil war, which has been brewing on-and-off since 2004, including the period of Arab Spring in 2011.
Hezbollah (Shi'ite) and Iran (Shi'ite) assist the insurgent Houthis (Shi'ite) against the Sunni government.
Al Qaeda has used the chaos in Yemen to establish bases there; hence the United States often targets al Qaeda operatives (by drone strike) in Yemen.
In January 2015, the Sunni president of Yemen resigned, under pressure from the Houthi Shi'ite rebel group which was supported by Shi'ite Iran.
In March 2015, Saudi Arabia (Sunni) launched an attack by a coalition of 9 countries (all Sunni) to support the Sunni government against the Houthi (Shi'ite) rebels. The United States has supplied weapons to the Sunni government and prevented weapons going to the Shi'ite Houthi rebels, including a military seizure by the U.S. Navy of an enormous arms shipment in the northern Arabian Sea in May 2021.
- NEWS: Latest statements on the Yemen Civil War from presidential candidates and political pundits
MIDEAST CONFLICTS NOT BASED ON SHIA-SUNNI SPLIT:
- Afghanistan is 15-20% Shia; the Taliban rulers are Sunni. The long ongoing trouble in Afghanistan does not fit the Shia-Sunni paradigm; this is an ethnic conflict, not a religious conflict.
- Kuwait is 30-40% Shia but rulers are all Sunni. Kuwait was a close ally of Iraq during the Iran–Iraq War
(that made sense using the Shia-Sunni paradigm, but Saddam's invasion of Kuwait was not on the grounds of Sunni-Shia split -- it doesn't explain EVERYthing!)
- Pakistan might someday have Sunni-Shia trouble, but their primary enemy is India, their Hindu neighbor.
India and Pakistan were one country until the 1940s, when they split into two countries along religious lines, one Muslim country and one Hindu country (Pakistan later split into a 3rd country, Bangladesh).
They have had several wars since then, focusing mostly on the Kashmir region, which both countries claim because it has a mixed religious history
(Kashmir's ruler was Hindu but its majority was Muslim at the time the two countries split). Same story, different labels.
- Nigeria, like most countries in West Africa, is Muslim in the north (near the Sahara) and Christian in the south (near the Atlantic Ocean).
Boko Haram is the Islamic terrorist group fighting against Western influence ("Boko Haram" means "Westernization is sacrilege").
Boko Haram is Sunni, and was affiliated with al Qaeda until they pledged allegiance to ISIS in March 2015.
The group is most infamous for the April 2014 kidnapping of 276 schoolgirls.
While the group is Muslim, and are commited to creating a Caliphate, they focus on the Muslim-Christian split in sub-Saharan Africa rather than the Sunni-Shia split in the Mideast.
Readers should not think that these sorts of religion-based wars are unique to the Islamic world.
In the Christian world, we have the same sort of split between Protestants and Catholics:
For example, when Northern Ireland (majority Catholic) was ruled by Great Britain (majority Protestant) a war ensued for decades.
And even in America, when John F. Kennedy (the first Catholic president) was elected in 1960, anti-Catholic sentiments resounded among the Protestant American majority.
Religious sectarianism among Christians doesn't justify religious sectarianism among Muslims -- but it does make it easier to understand!
Syrian Civil War (2011-2024)
 The civil war in Syria has been raging since March 2011, and has killed many tens of thousands of people (approximately 93,000 as of June 2013).
It is the latest result of the Arab Spring.
The civil war in Syria has been raging since March 2011, and has killed many tens of thousands of people (approximately 93,000 as of June 2013).
It is the latest result of the Arab Spring.
In 2011, the Arab Spring was running strong in several countries but has mostly played out now -- except in Syria.
At issue is whether President Assad (a dictator, not an elected president) should stay in power.
Two years ago, at issue was whether Assad would implement reforms, but he declined, so the rebels demanded his ouster instead.
The rebels were making progress until Hezbollah joined in, early in 2013
(Hezbollah is the terrorist group that rules Lebanon with Assad's help) -- that turned the tide in favor of Assad.
President Obama had previously established a "red line" that if Assad used chemical weapons, the U.S. would join the fight.
Obama declared that the "red line" had been crossed in June 2013.
The US, British and French had been aiding the rebels already, but only been sending "humanitarian aid" (food and medicine);
as of June 2013 the US is sending "military aid" (small weapons).
The Russians back Assad (who has plenty of Russian weapons already, including jets and tanks).
So in effect, the U.S. is now fighting a "proxy war" against Russia and Hezbollah in Syria.
Some proponents suggest that the US, UK, and France impose a "no-fly zone" in Syria --
using allied Air Forces to enforce agaisnt the Syrian Air Force.
That was done in Libya successfully -- the rebels won with allied air support.
Some opponents point out that the rebels' loose coalition -- called the Free Syrian Army --
has some groups which are affiliated with Al Qaeda.
U.S. aid has always "vetted" each group receiving aid, with the purpose of avoiding giving anything to Al Qaeda.
But of course materiel gets shared and some U.S. arms may end up in Al Qaeda hands.
NEWS: Latest statements on the Syrian Civil War from presidential candidates and political pundits
The War on Terrorism
 On Sept. 11, 2001, terrorists hijacked four commercial jets from Boston and Washington, and flew them into the World Trade Center in NYC and the Pentagon outside DC, destroying the Twin Towers and killing over 6,000 people. It was the worst terrorist incident in history.
Pres. Bush appointed Tom Ridge as the "terrorism czar," formally creating a cabinet-level post for a new Office of Homeland Security, initially funding it with $40 billion.
NATO invoked Article 5 of its charter, which commits 18 European allies to military action in response to an attack on the homeland of the US.
The primary suspect was Osama bin Laden, an exiled Saudi millionaire based in Afghanistan.
The CIA formerly funded bin Laden as a leader of the mujaheddin, or freedom fighters, when the Soviet Union occupied Afghanistan through the 1980s.
Bin Laden turned against the US when troops were stationed in Saudi Arabia during the Gulf War in 1990. He issued a fatwa, or religious edict, calling for the removal of US troops from the Holy Lands of Mecca and Medina (details below under Al Qaeda).
Bin Laden's organization, al Qaeda, which means "The Base," funds terrorist training and operations, and has been implicated in past terrorist actions in the 1993 World Trade Center bombing, the 2000 USS Cole bombing, and the 1998 simultaneous attack on two US embassies in Kenya and Tanzania.
The US responded to the embassy bombings by a cruise-missile attack aimed at bin Laden, terrorist training camps in Afghanistan, and chemical factories in Sudan. The US also by indicting bin Laden in US criminal court.
The Taliban was the Muslim fundamentalist political party which rules most of Afghanistan. They were the largest army of the mujaheddin, and were also funded by the CIA in the 1980s. Their leader was Mullah Mohammad Omar.
The Taliban ruled under Shari'ah, or Islamic law as described in the Koran, which implies strict interpretation of moral codes and numerous personal restrictions.
A portion of Afghanistan was ruled by the Northern Alliance, another mujaheddin group. Their leader was assassinated in the week preceding the World Trade Center attack; it is unknown whether there was a connection.
The exiled king of Afghanistan, Muhammad Zahir Shah, agreed to participate in a coalition government if the Taliban is overthrown. King Zahir is 86 years old, and has resided in Rome since 1973.
On Sept. 11, 2001, terrorists hijacked four commercial jets from Boston and Washington, and flew them into the World Trade Center in NYC and the Pentagon outside DC, destroying the Twin Towers and killing over 6,000 people. It was the worst terrorist incident in history.
Pres. Bush appointed Tom Ridge as the "terrorism czar," formally creating a cabinet-level post for a new Office of Homeland Security, initially funding it with $40 billion.
NATO invoked Article 5 of its charter, which commits 18 European allies to military action in response to an attack on the homeland of the US.
The primary suspect was Osama bin Laden, an exiled Saudi millionaire based in Afghanistan.
The CIA formerly funded bin Laden as a leader of the mujaheddin, or freedom fighters, when the Soviet Union occupied Afghanistan through the 1980s.
Bin Laden turned against the US when troops were stationed in Saudi Arabia during the Gulf War in 1990. He issued a fatwa, or religious edict, calling for the removal of US troops from the Holy Lands of Mecca and Medina (details below under Al Qaeda).
Bin Laden's organization, al Qaeda, which means "The Base," funds terrorist training and operations, and has been implicated in past terrorist actions in the 1993 World Trade Center bombing, the 2000 USS Cole bombing, and the 1998 simultaneous attack on two US embassies in Kenya and Tanzania.
The US responded to the embassy bombings by a cruise-missile attack aimed at bin Laden, terrorist training camps in Afghanistan, and chemical factories in Sudan. The US also by indicting bin Laden in US criminal court.
The Taliban was the Muslim fundamentalist political party which rules most of Afghanistan. They were the largest army of the mujaheddin, and were also funded by the CIA in the 1980s. Their leader was Mullah Mohammad Omar.
The Taliban ruled under Shari'ah, or Islamic law as described in the Koran, which implies strict interpretation of moral codes and numerous personal restrictions.
A portion of Afghanistan was ruled by the Northern Alliance, another mujaheddin group. Their leader was assassinated in the week preceding the World Trade Center attack; it is unknown whether there was a connection.
The exiled king of Afghanistan, Muhammad Zahir Shah, agreed to participate in a coalition government if the Taliban is overthrown. King Zahir is 86 years old, and has resided in Rome since 1973.
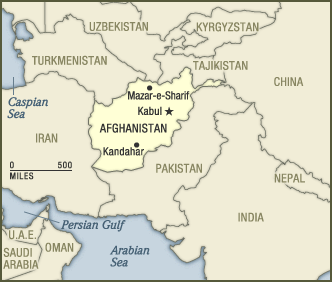
Afghanistan's neighbors are:
- Pakistan (which shares the Afghan ethnicity of Pashtun in its northern provinces);
- Iran (which shares the Northern Alliance's religion of Shi'a Islam);
- Tajikistan (a former Soviet republic, which also has a Shi'a minority);
- Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan (two other former Soviet republics; they are majority Sunni Muslim, like the Taliban);
- and China (bordering its Muslim province, known as Xinjiang in Chinese and Uighurstan in Arabic, where there are regular Islamic uprisings).
The Taliban is recognized only by Pakistan; Saudi Arabia and Yemen, the only other countries to have recognized the Taliban, severed diplomatic ties in late September.
Pakistan supplied the mujaheddin before and after the Soviet occupation. Complicating relations with the US, Pakistan exploded a nuclear device in 1998, in response to India's doing so. India and Pakistan have been fighting a sporadic war for decades over the Kashmir region.
NEWS: Latest statements on Afghanistan from presidential candidates and political pundits
Al Qaeda
- The document which Al Qaeda provides for its fighters is entitled "Declaration of Holy War Against the Country's Tyrants."
- It states in the introduction that Al Qaeda exists to end the occupation of the Muslim lands by "colonialists" and "infidels," which began on March 3, 1924.
- That date is when the Ottoman Empire (modern-day Turkey, who lost WWI alongside Germany) was divided up by England and France (the "colonialists" who occupied the Middle East until after WWII, which by extension includes Israel).
- The "infidels" refers to the modern Arab rulers of the region, whom Al Qaeda curses as its enemies, specifically calling for attacks on the rulers of Egypt, Syria, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia.
- Al Qaeda believes that the modern rulers of Muslim countries ("the apostate rulers") have turned away from Islam, and instead "aimed at producing a wasted generation that pursued everything that is western." The solution, Al Qaeda claims, is that "young men return to Allah" and "realize that Islam is not just performing rituals but a complete system: religion and government, worship and Jihad, ethics and... the Koran and the sword."
- In summary, Al Qaeda believes in ousting the rulers of Muslim countries whom they consider insufficiently Muslim. That especially includes Israel and the United States, who (in Al Qaeda's view) occupy the Muslim holy lands of Jerusalem (the capital of Israel), and Mecca and Medina (in Saudi Arabia, where the U.S. has military bases). But Al Qaeda's goal is to overthrow all leaders of the region, including Muslim leaders, in order to re-establish what they consider proper Islamic countries.
- While Al Qaeda's manual does criticize western values, its purpose is to advocate for Islamic rulers. Nowhere does the Al Qaeda manual discuss "hating what America stands for," nor does it even mention the United States -- Al Qaeda's purpose is to expel all non-Islamic rulers from Muslim lands.
Persian Gulf

- The Iraq War formally ended on Dec. 15, 2011. Approximately 5,000 "security contractors" will remain to guard the US Embassy in Baghdad, plus several thousand more "general support contractors." Another 9,000 US troops are just over the border in Kuwait.
IRAQ HISTORY:
- Throughout most of the 1980s, Iran and Iraq fought a bloody war. It ended with no border changes, and without any US intervention.
- In 1990, Saddam Hussein invaded Kuwait, claiming it as a province of Iraq. The US and numerous allied assembled by Pres. George H. W. Bush built up a counterforce in Saudi Arabia and succeeded in 1991 in pushing Saddam's army out of Kuwait.
- On the 10th anniversary of the Gulf War, President-elect George W Bush declared Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein "a big threat" and said he must be contained - by military force if necessary.
- In Jan 2001, outgoing President Clinton signed and transmitted to Congress a report on the provision of assistance to the Iraqi opposition. The report outlines plans for the transfer of humanitarian assistance for the relief of the Iraqi people and for radio and television broadcasting by the Iraqi National Congress (INC). The report also identifies certain issues that must be resolved in relation to implementation of those plans.
- The primary purpose of the provision is to assist those Iraqis who have been displaced from their homes or who are not receiving adequate assistance from the UN and other assistance organizations.
- Kuwaiti society is still deeply conservative. A strong Islamic current runs through the country-Islamists are fairly well represented in parliament and there is the odd Islamic extremist attack, against video stores or women not wearing the veil.
- NEWS: Latest statements on Iraq & Kuwait from presidential candidates and political pundits
Iran
- In April 2015, the US and Iran, alongside the rest of the U.N. Security Council, agreed on a "nuclear treaty": limiting Iran's nuclear enrichment; monitoring by the IAEA; and ending sanctions against Iran.
- Addressing the U.S. Congress in March 2015, the Israeli Prime Minister opposed the plan, saying that the deal is insufficiently restrictive.
- Most of President Obama's opponents, and many Republicans, concur with the hard-line Israeli stance that any deal with Iran is insufficient unless Iran recognizes Israel's right to exist.
IRAN NUCLEAR PROGRAM:
- In November 2011, the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Board of Governors criticized Iran after an IAEA report concluded that before 2003 Iran likely had undertaken research and experiments geared to developing a nuclear weapons capability.
- A number of Western nuclear experts have stated there was very little new in the report, that it primarily concerned Iranian activities prior to 2003.
- Iran rejected the details of the report and accused the IAEA of pro-Western bias.
- The IAEA Board of Governors has found Iran in non-compliance with its Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty safeguards agreement.
- Iran says its nuclear program is peaceful. Iran also claims that it was forced to resort to secrecy after US pressure caused several of its nuclear contracts with foreign governments to fall through.
President Obama announced the finalized nuclear deal with Iran in July 2015, after a seven-country negotiation (the United States, China, France, Germany, Iran, Russia, and the United Kingdom):
- Iran will reduce its stockpiles of enriched uranium
- Iran will limit enrichment equipment and facilities
- Iran will provide access for inspection about compliance
- The UN, US, and EU will remove economic sanctions against Iran.
- Iran and the US exchanged prisoners (5 US citizens in Iran and 14 Iranians in the US imprisoned for violating the sanctions)
- NEWS: Latest statements on Iranian Nuclear Weapons from presidential candidates and political pundits
Israel & Palestine

- 1948: The UN partitioned British Palestine into a Jewish state (Israel) and an Arab state (Palestine).
Six Arab countries declared war on Israel; Israel survived with borders different than those drawn by the UN; these are now known as the "pre-1967 borders."
Palestine did not survive; the East Bank and West Bank of the Jordan River were taken over by Jordan, and the Gaza Strip was taken over by Egypt.
Many Palestinians became refugees in the 1948 war; they have still not been resettled and are the subject of the current debate on "right of return."
- 1956: Britain, France, & Israel invaded Egypt to force open the Suez Canal; they briefly occupied the Sinai Desert until pressured by the US and UN to withdraw.
- 1967: Israel won the "Six Day War" and occupied Gaza & Sinai (from Egypt); the West Bank (from Jordan); and the Golan Heights (from Syria).
Jerusalem, split in 1948 between Israel & Palestine (and then Jordan), was unified under Israel; they annexed the whole city in 1980.
- 1973: A bloody war ended with no changed borders, but established the groundwork for an Egyptian-Israeli peace treaty in 1979.
Egypt's president, Anwar Sadat, shared with Israel's Menachem Begin the Nobel Peace Prize in 1980 for his efforts, but paid for it with his life in an assassination in 1981.
As part of the Egyptian peace treaty, Israel withdrew from Sinai (but not Gaza).
The shaky peace has held up since, with regular US intervention and billions of dollars of annual US aid to both Egypt and Israel.
- 1982: Israel invaded Lebanon in response to terrorist attackes by the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO).
Israel surrounded the Lebanese capital, Beirut, forcing the PLO and its chairman, Yasir Arafat, to withdraw.
Israel began its withdrawl from Lebanon in 1985; Syria still occupies parts of the country.
Israel also began establishing settlements on the West Bank in the late 1970s, which are a major point of contention in today's peace negotiations.
- 1987: Palestinians in Gaza and the West Bank began an uprising against Israel, called "the Intifadeh."
The PLO's Arafat signed a peace treaty with Israel in 1993, granting Palestine eventual self-rule in Gaza and the West Bank
-- this is the peace treaty which is still being phased in today. Jordan also signed a peace treaty with Israel, in 1994.
- 1996: Arafat is elected president of the "Palestinian Authority", and renounces the PLO Charter's clause calling for the destruction of Israel.
In 1998, the Wye River Accords (under Pres. Clinton) negotiated further Israeli withdrawal from the West Bank.
In 2000, a "Second Intifadeh" began in the West Bank; it continues today.
- Israel made peace with Egypt in 1979, and that peace treaty survived the Arab Spring uprising in Egypt in 2011. Israel signed a peace treaty with Jordan in 1994, and now has normalized relations with that neighbor. Israel made peace with the PLO in 1993, and granted autonomy to the Palestinian Authority. That entity split in 2007 into Fatah governing the West Bank (at peace with Israel) and Hamas governing the Gaza Strip (with regular rocket fire into Israel through 2014).
- AIPAC is the American Israel Public Affairs Committee, founded in 1951. The pro-Israel group, with 100,000 grassroots members nationally, is currently considered one of the most powerful lobbying groups in Washington.
Detractors claim that AIPAC support causes politicians to support Israel. Supporters claim that supporting Israel makes sense since it is the only stable democracy in the Middle East.
History of Yugoslavia
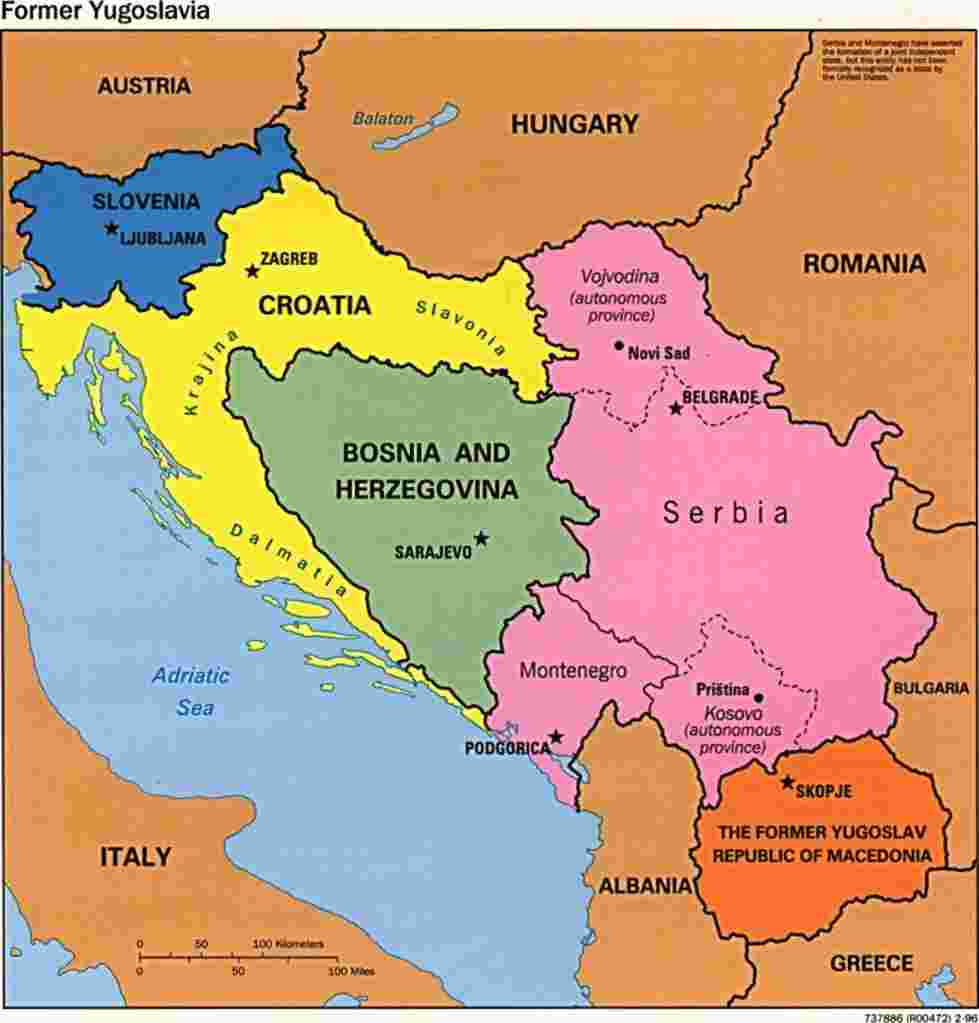 Yugoslavia was created after WWI, from a federation of Balkan countries.
The intention was avoiding further Balkan wars like those which ignited WWI.
After WWII, its borders were redrawn with six republics plus two provinces within Serbia.
(click on the map below left for an enlarged view).
Yugoslavia was created after WWI, from a federation of Balkan countries.
The intention was avoiding further Balkan wars like those which ignited WWI.
After WWII, its borders were redrawn with six republics plus two provinces within Serbia.
(click on the map below left for an enlarged view).
Sovereignty
The six Yugoslav republics (see below) have all had history as independent nations.
The two provinces within Serbia (Kosovo and Vojvodina) were never independent,
with legal status like California within the US. Hence much of the debate on Kosovo centers on 'sovereignty' --
attacking Kosovo can be viewed as an attack on the sovereignty of Serbia while it was involved in a Civil War.
Bosnia, on the other hand, had autonomous legal status like Puerto Rico within the US.
Bosnia had declared independence from Serbia before the US sent troops there, and hence sovereignty was not an issue.
Marshal Tito
Marshal Tito was the Communist leader of Yugoslavia since WWII.
He is credited with holding the Yugoslav republics together (by dictatorial force),
and after he died in 1980 the republics began to clamor for more autonomy.
Further pressure for independence came from the fall of the Soviet empire in 1989.
Breakup of Yugoslavia
In 1990, a new Yugoslav Constitution was enacted.
Four republics soon declared independence, leaving 'Rump Yugoslavia' as only Serbia plus Montenegro.
Status of the former Yugoslav republics and provinces:
- Slovenia: Declared independence in June 1991; one-week war with Serbia (a 'bloodless' war because Serbia focused on Croatia); Slovenia is now a prospering nation with hopes of joining NATO.
- Croatia: Declared independence in June 1991; longer war with Serbia; heavily involved with Bosnia war.
- Macedonia: Declared independence in Nov. 1991; avoided war because of arrival of international forces (including US forces, which are still based there).
Greece has blocked full international recognition because the name 'Macedonia' is also the name of a Greek province.
- Bosnia-Herzegovina: Declared independence in 1992; lengthy war with Serbia and Croatia, with all three countries involved in 'ethnic cleansing.' The war ended with the Dayton Peace Accords in 1995.
US forces are still stationed in Bosnia, which is partitioned into three ethnic regions (Serb, Bosnian, & Croat).
- Montenegro: Still part of Yugoslavia as an autonomous Republic.
Montenegrins are ethnically identical to Serbs; they differ only by geography. But in the wake of the Kosovo war, Montenegro may declare independence.
- Serbia: Legally, Serbia is just one republic of Yugoslavia. But the Serbs have always been the dominant group in all of Yugoslavia since is formation.
- Kosovo: Remains a province within the republic of Serbia. Its population is 3/4 Albanian (referred to as 'ethnic Albanians' to differentiate from residents of the neighboring country of Albania).
- Vojvodina: Also remains a province within the republic of Serbia. Its population is 1/2 Hungarian (they border Hungary, and prior to WWII were part of that country).
Slobodan Milosevic
Milosevic came to power as Chairman of the Communist Party in 1986.
His popularity increased greatly in 1987 after a speech in Kosovo strongly advocating Serbian nationalism
(the speech was made on the site of a 14th century battlefield. This is the political basis for Milosevic not granting Kosovo independence).
Milosevic was democratically elected President of Serbia in 1989, and elected as President of Yugoslavia in 1997.
He was indicted as a war criminal in June 1999, the first time a sitting President has been indicted.
His alleged crimes include genocide and ethnic cleansing.
In October 2000, Milosevic lost the presidential election to Vlajislav Kostunica. Milosevic gave up power after widespread protests and Russian urging.
In April 2001, Milosevic surrendered to Serbian government forces. He faces extradition to an international tribunal as well as domestic charges.
Religion and Ethnicity
The major religious divisions in Yugoslavia explain much of the political divisions:
- Eastern Orthodoxy is the religion of the Serbs, Macedonians, and Montenegrins.
Hence Russia (who are also Eastern Orthodox and ethnically Slavic) support the Serbs,
and Greece (who consider Macedonians ethnically Greek) identifies with Macedonia.
- Roman Catholicism is the religion of the Croats, Slovenes, and Hungarians.
Hence Croatia and Slovenia are religiously distinct from Serbia even though they are all ethnically Slavic.
- Islam is the religion of the Bosnians and the Albanians (including those in Kosovo).
Hence the country of Bosnia-Herzegovina is all ethnically Slavic but has three distinct religious groups.
Kosovo
In 1999, the US and NATO negotiated with Milosevic in Rambouillet, France, attempting to resolve the Kosovo crisis without ethnic cleansing or war.
The goal was to be a 'Rambouillet Agreement' fashioned after the Dayton Agreement that ended the war in Bosnia.
The peace talks failed, and NATO bombed Serbia and Kosovo from March to June 1999.
Milosevic capitulated; the Serbian Army left Kosovo; and NATO, Russian, and UN troops are now stationed there under the 'KFOR' banner.
Click for Amazon books on War & Peace:
The Operators: Inside America's War in Afghanistan
Embracing Israel/Palestine
Israel vs. Iran: The Shadow War
War Journal: My Five Years in Iraq
Click for citations and references on 2024 War & Peace:
- Department of Homeland Security press release, Statement from Secretary Mayorkas on the Anniversary of Russia's Unprovoked Invasion of Ukraine, February 24, 2023.
- FAIR (Fairness and Accuracy in Reporting), Calling Russia's Attack 'Unprovoked' Lets US Off the Hook), by Bryce Greene, March 4, 2022
Click for citations and references on 2020 War & Peace:
- The Hill, "War in the Caucasus: What happens without US leadership," by Stephen Blank, 10/20/20
- International Crisis Group, "Chechnya: The Inner Abroad," 30 June 2015
- State Department press release, "Crimea Is Ukraine," by Michael R. Pompeo, Secretary of State, February 26, 2020
- Brookings Institute, "Crimea: Six years after illegal annexation," by Steven Pifer, March 17, 2020
- The Guardian, "Trump's Afghanistan withdrawal announcement takes US officials by surprise," Emma Graham-Harrison and Julian Borger, 8 Oct 2020
- Friends Committee, "Costs of War: By the Numbers," March 15, 2011
- N.Y.Times, "U.S. Sending More Troops to Syria to Counter the Russians," by Eric Schmitt, Oct. 26, 2020
- Brookings Institution, "A European security force in Syria is a courageous idea," by Constanze Stelzenmueller, October 30, 2019
- Military Times, "US plans further troop reductions in Iraq by November," by Robert Burns, August 30, 2020
- North Atlantic Traty Organization, "NATO and Afghanistan," 13 Oct. 2020
- Quartz, "The legality of targeting Soleimani depends on these questions," by Ephrat Livni, January 9, 2020
- Jurist.org, "The Killing of General Soleimani--A Blatant Violation of International Laws," by Archit Shukla, April 14, 2020
- Times of Israel, "Plans for over 2,700 more settlement homes advanced--making 5,000 in 2 days," 15 October 2020
- Palestine U.N. Observer, "Israeli Settlements and Other Violations," 15 October 2020
- Reuters, "Why is the U.S. moving its embassy to Jerusalem?," by Stephen Farrell, May 7, 2018
- Vox.com, "The controversial US Jerusalem embassy opening, explained," by Alexia Underwood, May 16, 2018
|
 The civil war in Syria has been raging since March 2011, and has killed many tens of thousands of people (approximately 93,000 as of June 2013).
It is the latest result of the Arab Spring.
The civil war in Syria has been raging since March 2011, and has killed many tens of thousands of people (approximately 93,000 as of June 2013).
It is the latest result of the Arab Spring.



 Yugoslavia was created after WWI, from a federation of Balkan countries.
The intention was avoiding further Balkan wars like those which ignited WWI.
After WWII, its borders were redrawn with six republics plus two provinces within Serbia.
(click on the map below left for an enlarged view).
Yugoslavia was created after WWI, from a federation of Balkan countries.
The intention was avoiding further Balkan wars like those which ignited WWI.
After WWII, its borders were redrawn with six republics plus two provinces within Serbia.
(click on the map below left for an enlarged view).